Home Industry Crypto and virtual money Hot Wallet vs. Cold Wallets: W...
Crypto And Virtual Money

CIO Bulletin
17 December, 2025
Key Takeaways
Cold wallets are offline and provide the highest level of security, making them ideal for long-term storage of large cryptocurrency holdings.
Hot wallets are online and convenient for frequent transactions but are more vulnerable to cyber threats.
Coinbase and MetaMask are examples of hot wallets, while Ledger and Trezor are popular cold wallet options.
Using both wallet types together can balance security and convenience by storing most assets in a cold wallet and smaller amounts in a hot wallet.
Choosing between a hot wallet and a cold wallet is one of the most important decisions you’ll make for protecting your crypto assets. While both options store cryptocurrency, they differ greatly in security, accessibility, and how you manage your funds. Apart from wallet choice, selecting an exchange with competitive fees and bonuses is also necessary.
In this article, we'll discuss the key differences between hot and cold wallets, break down how each option works, and help you understand the safety considerations for both. We'll also discuss how you can combine hot and cold wallets, so you can choose the right storage method based on your total assets, risk tolerance, and trading platform.
A hot wallet stores your crypto keys online so you access funds fast. You use a hot wallet to send, get, and manage crypto through an app, browser, or computer. Because the wallet stays connected to the internet, actions happen in real time, which suits daily use and frequent transfers.
Hot wallets work through software. When you approve a transaction, the wallet signs it with your private key and sends it to the blockchain. This speed explains why many users start here. The tradeoff involves exposure. Online access raises risk from phishing, malware, and account takeovers, so you keep smaller balances here.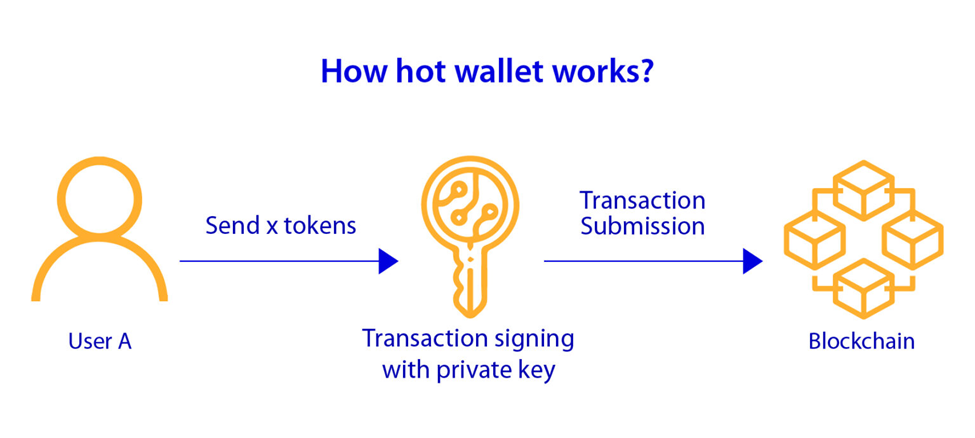
Popular hot wallets include MetaMask for Ethereum and tokens, Coinbase Wallet for easy exchange access, and Trust Wallet for broad coin support. Use hot wallets for spending and trading. Move larger holdings elsewhere for storage.
Mobile Wallets: These are apps installed on smartphones, offering convenience and accessibility anytime, anywhere. Reliable mobile wallet like Trust Wallet and MetaMask are popular choices. MetaMask, in particular, has gained traction due to the Ethereum surge, as it supports Ethereum-based tokens and decentralized applications (dApps).
Desktop Wallets: Installed on personal computers, desktop wallets provide a balance between security and usability. Examples include Exodus Wallet, which supports multiple cryptocurrencies, and Atomic Wallet, known for its user-friendly interface and staking features.
Web Wallets: These wallets are accessed through web browsers, offering seamless integration with cryptocurrency exchanges. Coinbase Wallet is a prime example, allowing users to manage their assets while interacting with the Coinbase exchange.
Hardware Wallets: Although primarily considered cold wallets, some hardware wallets can function as hot wallets when connected to the internet. Devices like Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T are among the best cold wallets for crypto, offering enhanced security while enabling online transactions when needed.
A cold wallet is a crypto wallet built for offline storage. It keeps private keys away from the internet, which lowers exposure to online attacks. This setup explains the core difference between hot and cold wallet use. A hot wallet supports speed. A cold wallet focuses on protection. In short, a cold wallet is cold storage for crypto assets.
Cold wallets suit long- term holding. You store keys offline, then sign transactions without constant internet access. When you want to move funds, you connect the wallet briefly or transfer assets to a hot wallet. This extra step slows access, yet it adds a strong layer of safety. For large balances, this tradeoff matters.
Cold storage reduces risk from phishing, malware, and exchange breaches. Control stays with you. No third party holds your keys. This level of control attracts users who treat crypto as savings, not spending money. Many holders pair cold storage with a best crypto hot wallet for daily use, then move funds back offline after activity.
Top cold wallets include Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T, and KeepKey. These devices use secure chips, PIN protection, and recovery phrases. If a device gets lost, recovery words restore access. This design protects funds even during hardware failure.
Cold wallets work best for users who value security over speed. If you rarely move assets, offline storage fits. If you trade often, you use cold storage as a vault, not a tool.
Hardware wallets. Hardware wallets store keys on a physical device. You connect the device only when signing a transaction. The keys never leave the device. Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T lead this category. They offer strong protection while keeping setup manageable. This option suits most long-term holders.
Paper wallets. A paper wallet stores keys on printed paper. No digital trace exists after creation. This approach removes online risk, though physical damage or loss creates danger. Fire, water, and theft matter here. Paper wallets suit users who want offline storage without devices and who store keys securely.
Air gapped devices. Air gapped wallets run on devices with no internet connection. Data moves through QR codes or removable media. This isolation blocks remote attacks. Advanced users favor this method for high value storage, though setup takes more effort.
Deep cold storage. Deep cold storage places keys in secure physical locations like vaults or safety boxes. Access requires planned steps and verification. Institutions and large holders use this method to protect major holdings.
The key difference between hot and cold wallets is their connectivity and purpose. Hot wallets stay connected to the internet, which is ideal for frequent trading and easy access. In contrast, cold wallets are offline and safer for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies as they are not exposed to online attacks .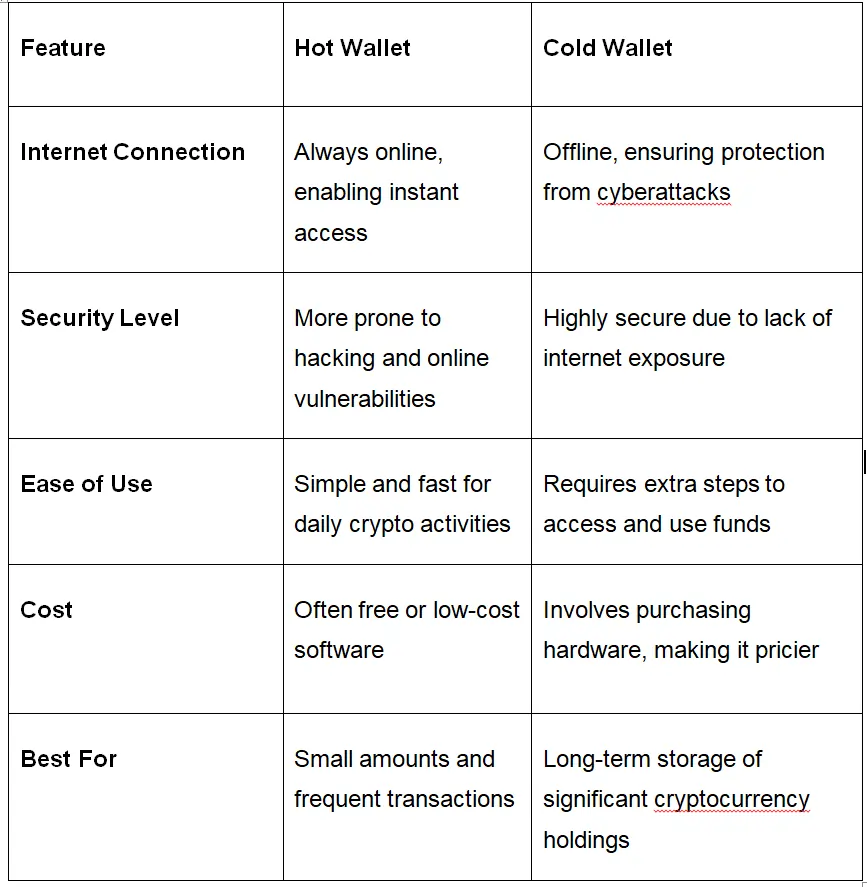
Choosing between hot wallet vs cold wallet depends on your priorities: security or convenience. Let’s explore the differences to help you decide.
Cold wallets are considered the safest option for storing digital assets. Operating in cold storage, they remain offline, making them immune to online threats like hacking, phishing, and malware. This makes cold wallets ideal for long-term storage of large cryptocurrency holdings. If security is your top priority, a cold wallet is the way to go. However, accessing funds stored in a cold wallet requires extra steps, such as connecting the device to an online platform or manually entering private keys.
In contrast, hot wallets are designed for quick and easy access. Always connected to the internet, they are perfect for frequent transactions and managing smaller amounts of cryptocurrency. However, this constant connectivity increases their vulnerability to cyberattacks, such as hacking and unauthorized access. If you use a hot wallet, it’s essential to use two-factor authentication, use strong passwords, and keep your software updated to minimize risks.
Combining hot and cold wallets gives you balance between access and protection. You use a hot wallet for daily activity, and you keep a cold wallet for storage. This setup limits exposure while keeping funds available when needed.
Here is how most experienced users handle it. You store small amounts in a hot wallet for trading, spending, or transfers on crypto trading platforms. You move larger balances to cold storage after each session. If a hot wallet gets compromised, losses stay limited.
This approach also builds better habits. You pause before moving funds from cold storage and review addresses and amounts. Fewer rushed actions reduce mistakes. Cold storage acts as a barrier against impulse moves and scams. You do not need complex tools. One hot wallet and one cold wallet cover most needs. Set clear rules for amounts and timing. Stick to them. This method protects assets without slowing everyday use.
Cold wallets, like Ledger or Trezor, provide reliable security for long-term storage by keeping your assets offline. Hot wallets, such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet, provide quick access for frequent transactions but come with higher risks due to their online nature.
For the best balance, you can use both wallet types. Store the majority of your assets in a cold wallet for maximum security and keep smaller amounts in a hot wallet for daily use. This combination ensures your funds are protected while remaining accessible when needed. Clear rules for usage and regular reviews of your wallet strategy can further enhance your asset management.

Insurance and capital markets







